Saddle pulmonary embolism happens when a relatively large blood clot lodges inside or “saddles” the main pulmonary artery at its point of division, where it divides into the left and right lungs.
When a blood clot obstructs the blood vessel and is stuck inside it, this is known as an embolism. Additionally, when the blockage occurs inside the blood vessel of the lungs, it is known as a Typical Pulmonary Embolism.
Furthermore, it is a serious and life-threatening condition and leads to respiratory failure. The condition requires immediate medical attention, or it may turn fatal for the patient.
In this blog, we will be discussing saddle pulmonary embolism, its causes, risk factors, signs, and symptoms in detail. Additionally, we will also delve into the treatment and prevention options available for this condition.
What is Saddle Pulmonary Embolism?
Saddle pulmonary embolism is a sudden or acute pulmonary embolism. A large blood clot lingering at the intersection, where the major pulmonary artery divides and eventually branches off into the right and left lungs, causes this condition. This causes a right ventricular stain in the heart.
However, its occurrence is rare, accounting for only around 3 to 5% of all acute PE cases.
The vital function of pulmonary artery is to carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs, where it is filtered and becomes reoxygenated.
Due to the obstruction at the main pulmonary artery, where it is branched, blood flow is halted; as a result, Hypotension occurs or blood pressure deviates from the stable range. Consequently, this leads to inadequate blood supply to organs, such as the brain, heart, and kidneys, resulting in damage.
If urgent medical treatment is not given, saddle pulmonary embolism can also result in heart failure and sudden death.
Causes & Risk factors of Saddle Pulmonary Embolism
Furthermore, the American Society of Hematology explains that blood clotting seals wounds and prevents blood loss naturally. The body eventually breaks down and absorbs the blood clot into the bloodstream.
Nevertheless, blood clots can potentially cause numerous issues if they have formed without any injury or have not dissolved back into the bloodstream.
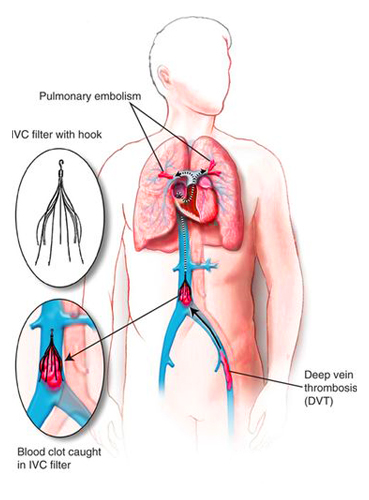
Furthermore, the most common reason behind pulmonary embolism is the blood clot that forms in the deeper veins of arms, legs, and pelvis. Deep Venous Thrombosis or DVT is the name of the condition.
Everyone can develop blood clots, but if we talk about incidence percentage, then men are at a higher risk of developing blood clots than women. Moreover, common risk factors of a blood clot of developing blood clots are mentioned below.
Increased Amount of Estrogen
If estrogen levels are elevated in the body, it consequently increases the risk of blood clotting. Some factors may result in the rise of estrogen levels such as;
- Pregnancy – it increases the risk of blood clots seven times.
- Childbirth – the risk of a blood clot is high after six weeks post delivery.
- Contraceptive pills – Along with hormonal medicines, contraceptives are likely to increase the risk of blood clotting.
- Hormonal Replacement Therapy – HRT is a type of therapy that regularizes the estrogen levels in your body. However, if taken beyond normal limits, it can cause blood clotting.
Decreased or Diminished Blood Flow
Furthermore, due to diminished blood flow, blood starts pooling in the blood vessels, which subsequently increases the danger of blood clots. This causes the body to go into shock. The elements that can cause reduced blood flow are as follows:
- Staying static for extensive periods of time because of persistent bed rest, trauma, or accidental injury.
- Sitting in the same position or at the same place for long periods of time, for example, during long journeys in an airplane or car.
- Wearing a fracture cast on the upper or lower limbs.
- Full or partial body paralysis.
Venous Injuries
Injury to any vein in the body can cause blood clotting. If the human body does not dissolve or split the blood clot and take it back into the bloodstream, it can deteriorate blood flow.
Additionally, blood clotting also will affect the passage of blood to different parts of the body. The factors behind venous injury can be fractures, serious muscle injury, or any type of surgery, especially hip replacement surgery
Severe and Chronic Medical Conditions
A few chronic medical conditions that can be potentially severe could increase the risk of blood clotting. Examples are mentioned below.
- Cancer: Cancer patients are generally at a higher risk of developing blood clots because of the nature of the disease itself.
- Heart diseases: Blood clots that form in the heart can lead to serious complications, such as a heart attack or stroke.
- Lung diseases: They can cause changes in the blood vessels in the lungs, making it easier for blood clots to form.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, can also increase the likelihood of blood clots. These conditions can cause inflammation and damage to the blood vessels, which can increase the risk of blood clots.
Several additional factors increase the risk of blood clot formation in the body, with notable connections to conditions like Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and saddle pulmonary embolism.
People with inherited clotting disorders like Factor V Leiden, as well as those with blood disorders or blood cancers, are particularly vulnerable.
Certainly, neglecting to take prescribed blood thinners heightens the risk, emphasizing the importance of adhering to medical advice.
Additional contributing factors include aging, smoking, obesity, and varicose veins
Signs and Symptoms
Some known signs and symptoms of saddle pulmonary embolism are as follows:
- Spontaneous dyspnea and shortness of breath
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Fainting or sudden loss of consciousness
- Palpitations
- Rapid and abnormal heartbeat
- Chest discomfort and pain
- Excessive sweating
- Coughing up and throwing blood
- Bluish and discolored nails and skin
Point to note
However, it is crucial to note and understand that the symptoms of a pulmonary embolism can be strikingly similar to those of a heart attack. Reach out to a health care professional if you experience any of these symptoms
Treatment for Saddle Pulmonary Embolism
Saddle pulmonary embolism requires immediate medical intervention. Things can go to the extent that a patient might need admission to the intensive care unit at the hospital.
The main goal of treatment is to disassemble the blood clot and resume normal blood flow to the lungs. Moreover, the aim of the treatment is to prevent blood clots from multiplying.
Furthermore, there are many treatment options available, and the doctor recommends them according to the patient’s condition.
Medications for Saddle Pulmonary Embolism
Physicians:
suggest these medicines to patients with Saddle Pulmonary Embolism to help alleviate the pain.
Anticoagulants:
Such class of drugs stop existing clots from multiplying and growing bigger. Additionally, anticoagulants put a halt to the new blood clot formation. These medicines can be administered via the intravenous route, or the patient can take them orally in tablet form.
Thrombolytics:
This category of medicine dissolves blood clots. Nonetheless, they can divulge a side effect which is bleeding. This is the reason why doctors usually avoid and only prescribe thrombolytics in fatal conditions such as Saddle PEs.
Procedures
However, when medical intervention fails, the health care professional performs some additional procedures to help manage the situation.
Vena Cava Filter:
This process includes the placement of a tiny metal filter within the largest vein of the body, known as the “vena cava”. It helps in preventing blood clots from reaching the lungs. Moreover, Vena Cava filter is important and helps people who are contraindicated to blood thinners.
Figure: In the operating room or interventional radiology suite, a medical professional inserts a catheter (tube) into the IVC from the groin or neck and uses contrast to scan the IVC. Furthermore, they guide the insertion of the filter into the IVC with the help of X-rays.
Percutaneous Thrombectomy:
A flexible, hollow tube is inserted inside the blood vessel known as a catheter. This helps in breaking the blood clot. There are two approaches to its use. First, is to suction up the blood clot into the catheter.
Second, is manually interjecting tiny instruments to split up the blood clots. A patient will be put under general anesthesia for the process of percutaneous thrombectomy.
Thrombolytics can treat blood clots, but they carry risks and complications, including life-threatening hemorrhage.
However, suction embolectomy offers an alternative for patients who cannot undergo anticoagulation and thrombolytic therapy due to certain contraindications.
This treatment for pulmonary embolism accesses the peripheral vasculature and removes the clot with a large-bore syringe while minimizing blood loss.
Additionally, by using suction embolectomy, patients can avoid the potential risks associated with thrombolytics and enjoy a safer treatment option.
Prevention of Saddle Pulmonary Embolism or Blood Clotting
According to the Disease Control Centre, people who are at the highest risk of developing blood clots can take the following precautions.
- Regular physical activity
- Weight maintenance
- Comfortable and loose clothing
- Movement post-injury or surgery
- Use of compression stockings
- Use of aspirin
All You Need to Know
While Saddle Pulmonary Embolism is a rare medical occurrence, it is also potentially fatal.
In saddle pulmonary embolism, a blood clot sits back at the bisecting point of the pulmonary artery, which is branched off into the right and left lungs.
Instant treatment is crucial to redeem the flow of blood to the lungs. Moreover, immediate medical intervention will prevent the chances of possible complications and inclusive death.
If you are suffering from any symptoms, you can visit Lung N Sleep Clinics in Michigan for a professional consultant.
Outlook of Saddle Pulmonary Embolism
Further, Saddle Pulmonary Embolism can result in fatal and life-threatening complications. Almost 2 in 6 people who suffer from pulmonary embolism die immediately. Consequently, the remaining 40% of patients die within the next month of diagnosis.
According to a study conducted in 2021 stated that out of 120 patients admitted with Saddle Pulmonary Embolism, 10% died while remaining in the hospital. the other 8 to 9% die within 6 months after being discharged from the hospital.
Moreover, the key factor in determining a patient’s outlook is whether treatment is initiated within the first few hours of the vessel obstruction. Early diagnosis and swift medical intervention can significantly reduce the severity and fatality of the disease, and patients can recover fully.
In treating saddle PE, healthcare providers typically administer anticoagulant injections for 5 to 6 days, then bridge patients to anticoagulant tablets for a further 3 to 4 months.
FAQs
How common is a saddle pulmonary embolism?
Saddle pulmonary embolism is an acute or sudden type of embolism that rarely occurs in humans. Hence, it only makes up about 2% to 5% of all pulmonary embolism cases.
What causes a saddle pulmonary embolism?
The medical condition occurs when a large blood clot blocks and prevents blood flow in the intersection. There, the main pulmonary artery divides into the left and right lungs causing the blood pressure to drop and insufficient blood flow to the organs.
What are the early warning signs of a pulmonary embolism?
Some early signs and symptoms include chest pain, fainting, shortness of breath, and coughing blood. Moreover, irregular heartbeat, dizziness, fever, excessive sweating, leg pain or swelling, and bluish or discolored skin are also major signs to monitor.
What is the survival rate of a saddle pulmonary embolism?
Patients who suffer from saddle pulmonary embolism die within a month of diagnosis. In some cases, the condition is so severe that they die instantly. However, if diagnosed and treated immediately, the survival rate gets higher.
How long does it take to recover from a saddle pulmonary embolism?
The time it takes to recover from saddle pulmonary embolism may differ from person to person. For some, it takes months or even years to get treated. However, some people may recover completely within weeks. Moreover, It depends on the severity of your disease.
How is a saddle pulmonary embolism removed?
It can be removed through the two most commonly used procedures. The Vena cava filter involves a small metal filter inserted inside the vena cava to prevent blood clots from reaching the lungs. Percutaneous thrombectomy, in which the doctor inserts a catheter to remove or break the blood clot. Furthermore, medications like thrombolytics dissolve the blood clots but might lead to bleeding.
Do lungs heal after pulmonary embolism?
Most people recover fully from pulmonary embolism, but some patients suffer long-term complications of PE. Furthermore, causing blood clots or chronic damage to the lungs.